Osteoarthritis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis) is the defeat of the knee joint mainly are not inflammatory in nature, that sees to the wear of the cartilage lining the knee joint and eventually to the destruction of cartilage deformation in the knee joint and limitation of motion. Therefore, it is important to be able to recognize the disease and know how and what to treat it.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint (the so-called still gonartrózaom – from the Greek for "whip" – knee) – is a progressive degenerative-degenerative defeat of the cartilage lining the surface of the joint, which sees the violation of his labour and pain feelings.
The causes of arthrosis of the knee joint
Gonarthrosis is divided into primary (arising independently) and secondary, which arises as a result of other diseases of the knee joint.
The primary
Osteoarthritis primary (genuinny) – is it osteoarthritis, starting without any appreciable cause and hitting the unaltered articular cartilage in many joints at the same time. Was observed more frequently in persons over 40 years. It is also proved that women are more often men suffer from joint arthritis suffering in the knee joints and the joints on the hands.
Why does primary osteoarthritis, until the end is found, but most likely lead to it metabolic disorders. It causes changes to the biochemical reactions that occur in the cartilage. Time collapses, degenerates and accumulates salt. The surface of the knee joint changes the structure of the cartilage, which sees in the knee accumulates fluid and appear cyst Becker.
Secondary
It is the result of disease helena damage to the joints, according to their clinical manifestations differ from the primary. Develops in virtually all joints.
Secondary osteoarthritis arises from the following reasons:
- the inflammatory process of immune helena infectious origin;
- dysplasia helena traumatic injuries of the meniscus helena of the knee joint (miniscope);
- fractures intra-articular bones which form the knee joint;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- tumors of the bones;
- ankylose spondylitis;
- osteoarthritis, occurring in diseases of the Paget.
Symptoms

The symptoms of osteoarthritis include the following:
- pain in the stop, the knees, the hip joints and the lower back;
- stiffness, stiffness and crunching in the joints;
- pain after sleep, helena a longer stay in one position;
- swelling of the joints;
- aches when the weather changes;
- pain in the joints after exertion;
- trauma – fractures, sprains, as well as damage to the meniscus;
- the increased load;
- overweight and obesity;
- weak ligamentous apparatus – disorderly ligaments;
- violation of the metabolic processes in the body;
- stress.
Deformation of the joint
Deformation of the joint is the change of the shape of the joint, caused by a shift of all the mating bones in dislocation, developing in the joint of pathological fabric growths. Most often deformation of the exposed joints on the arms, legs, lower limbs.
The deformation of the joints, usually becomes the result of complex metabolic disorders in periarticular, bone helena cartilage tissue, where they tend to accumulate atypical in this localization and the concentration of the substance.
The result of the deformation of joints often becomes a fusion of the joints, bony growths, subluxation of the joints and musculo-ligamentous apparatus.
In relation to this to ensure the basis of gonartrózaa apply symptomatic treatment, however, a comprehensive approach, aimed at eliminating the disorder in general, showing greater efficiency and warns of relapse.
The diagnosis of deformation of the joints is done without regard to the determination of the total diagnosis. She lies in the basis of the next survey and the overall conclusions. An objective examination of the joint allows to determine their configuration, swelling, soreness when feeling and movement, a range of active and passive movements in the joints and changes in skin and subcutaneous tissue in the area of the joints.
Limitation of motion of the joint
Emit different degrees of restriction of motion: from mild, barely noticeable violates the usual volume of movements, up to complete loss of mobility.
According to the degree of limitation of motion of the joint, we distinguish:
- Stiffness – a complete immobility of the diseased joint.
- Stiffness – maintained only a slight amount of moves. For example, a small rocking motion. During a survey of the stiffness is to be distinguished from the stiffness.
- Contracture – restriction of mobility lasting and significant, but still remains a certain range of motion in the joint. Diagnose range of movements is possible using a simple protractor.
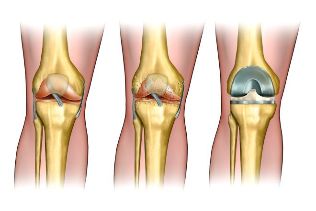
The degree of arthrosis of the knee joint
First. In this case, the disease is characterized by minor pain when performing active movements. Can accumulate synovial fluid in the cavity of the joint, which sees to the formation of Baker's cysts. Pain arise during the movement, but are held in peace. Cartilage fabric damage, but outwardly deformation of the joint invisible.
Second. Occurs, the joint space narrowing, cartilage substance gets damaged in a large extent. In the picture, which you will find in the course of the x-rays, you may notice a swelling of bones. Sharp pain accompanies any movement, which is involved in the knee joint. In idle state the unpleasant sensations persist, but then they appear again. To headaches it adds a distinctive crunch when committing the extensor movements.
Third. Sometimes the cartilage of the fabric becomes delicate, arise from the bare areas of bone. On the On the radiograph evident in the large number of osteophytes – sediments salt in the cavity of the joint. In addition, there can be detected a loose body.
Possible complications and consequences of arthrosis of the knee joint
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a degenerative disease that develops over time. Joint pain and stiffness are still so strong, that the patient is not able to cope with daily activities. Some people lose performance, when arthritis comes into such a stage, that the doctor only recommends surgery for joint replacement.
If you ignore the symptoms of the disease and not to hold early treatment, the likelihood of complications is fairly high.
The possible consequences of running osteoarthritis include:
- the critical deformation of the joint, its complete destruction;
- global impairment of motor functions;
- the appearance of intervertebral hernia;
- reduction in quality of life, loss of serviceability.
Which doctor deals with the treatment?
It may be a district therapist, surgeon, orthopedist. According to the needs of prescribe the consultation of a rheumatologist. Physician-rheumatologist surveys, You will determine the exact diagnosis will determine exactly what type of joints to be amazed. Prescribe laboratory and instrumental methods of diagnosis.
Only with the help of a complete examination of the expert will be able to answer the main research question: what stage gonartrózaa in a patient, and what treatment he needs.
In the presence of accompanying pathologies in the spinal column requires the advice of a neurologist and vertebrologist. These experts prescribe a restorative treatment, during which is removed painful due to compression of the nerve fibers in the intervertebral disks.
Diagnosis
Lesions of the joint, resembling arthritic, arise in many other diseases, and ignorant people are often mistaken in the definition of the disease. So in any case do not try to set the diagnosis yourself.
Instrumental examination
X-ray diagnostics – the most popular and meaningful method is due to its simplicity, availability and high value. Images are usually carried out in two planes – the lateral and direct, but if necessary can use a variety of specific stacking.
Ultrasound is considered to be quite promising direction, which allows to detect the liquid, put the assessment of pathologies of the soft tissues, and also imagine the cartilage and the articular surface. The advantages of this method before radiography is covered by the possibility to change the position of the sensor, and also the lack of need for strict positioning of the patient for a more standard projection.
MRI and computed tomography, which provide a large amount of information, as well as the possibility to obtain three-dimensional image of the examined area.
Laboratory analysis
When gonarthrosis pathological changes are found primarily in articular cartilage, but also subchondral bone, synovial packaging, other soft tissues of the joint. Because the opportunity to directly explore these patterns are limited, the most important sources for grasping the biological markers are blood, urine and synovial fluid.
In most cases, patients with joint arthritis suffering from knee joint missing changes in the analysis of blood and urine, except in cases of synovitis with significant effusion, when it appears the increase in ESR, hypergammaglobulinemia, increased levels of acute phase – CRP, fibrinogen, etc. In the investigation of synovial fluid significant differences from the current indicators do not reveal.
In recent years, an intensive search for possible biological markers (BM) degradation and repair of the tissue of the joints (mainly of cartilage and bone). BM reflect the dynamic changes are used as predictors of the forecasts of gonarthrosis and indent the effectiveness of pathogenetic therapy. The opening of a new and deeper study of the well-known BM to better understand the mechanisms of the pathogenesis of arthrosis.
But the main task by using biological markers of metabolism of cartilage – evaluation of the chondroprotective properties of drugs and monitoring of treatment medication belongs to the group of "modifying the disease".
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint
Treatment of arthrosis, to put it mildly, not exactly a simple task. So, before you begin their bitter struggle with this disease, be sure to find a good therapist, be surveyed for him and together with him create a treatment plan.
Products
You often receive medications for the alleviation of inflammation and painful sensations in osteoarthritis of the knee joint – it is anti-inflammatory drugs non-steroidal nature. Drugs effective in inflammatory processes, accompanied by synovitis. In addition, the above-mentioned drugs remove the pain. However, they do not cure alone disease.
When taking anti-inflammatory non-steroidal medication it is worth it to stick to all recommendations of the doctor because of these drugs, there are an impressive number of side effects, especially in long-term their application.
Chondroprotectors – it is a class of drugs, which restores the pain of the cartilage fabric. When the use of chondroprotectors is worth it to take into account that these drugs are maximally effective in the complex treatment of the disease.
Vasodilator drugs also appointed in complex treatment of arthrosis. By using them you are able to restore blood circulation in the joint, and also relieve the spasm of the small blood vessels.
As anesthetic resources are most commonly used ointments helena siding with the effect of heating up. When you need a quick relief, it may be shown, intra-articular injection of corticosteroid hormones.
Surgery
Puncture (minimally invasive intervention). This method is used for the diagnosis of the disease. In the joint capsule injected the needle, take away part of the liquid. This allows to obtain material for analysis, reduce the burden on the capsule, when it is necessary to specify the corticosteroids directly at the site of inflammation.
Arthroscopy. Represents the introduction of a special device the arthroscope through incisions in the skin. The method allows to carefully examine the joint, but also to remove the separated fragments of cartilage, which causes the inflammatory process and pain.
Periarticular osteotomy. The essence of the method lies in the administration of the bone with subsequent push them under a different angle. The operation allows to reduce the load on the joint and remove the pain for a long time. Despite its effectiveness, this type of surgical procedure applied rarely – too much of a burden on the body of the patient and long period of rehabilitation.
Joint. In cases where other treatments fail, and the disease is completely helena almost completely destroyed the joints, replacing them with prosthetics made of plastic, metal, helena ceramics.
Joint – is a difficult and expensive operation, which requires a longer rehabilitation. Many patients within a few months after surgery plague pain. At the same time, however, this method often is the only alternative to the immobility of the patient. The life of the modern prosthesis reaches twenty years, and all these years the patient may live a full life.

Recommended diet
Diet is necessary in the first place, in order to control your weight. It is proved that osteoarthritis often develops and the harder tolerated as it is in people with overweight, so:
- limit your drinking of alcohol, fatty foods, semi-finished products;
- monitor power mode;
- reduce the amount of salt consumed;
- reduce the amount of sweets;
- eat more vegetables and fruits (with an emphasis on seasonal).
Prevention of arthrosis
Main activities to prevent the development of gonarthrosis are:
- reduce excess body weight;
- increase physical activity;
- proper nutrition;
- compliance with the principles of HLS.
Leading a healthy lifestyle will enhance not exceeding your body, improve the condition of cartilage, joints and bones. It is necessary to give up alcohol and smoking. A lot of time to spend in the fresh air, experience less stress and experience, plenty of good mood and positive.
Osteoarthritis – a disease that does not recover completely, however, its development may stop, if it's time to pay attention to their health status, and proceed to treatment. Therapy can weaken helena even remove completely some of the symptoms, than to significantly facilitate the life of the individual patient.
















